Nurdles, The 5mm-Sized Plastic Pellet Destroying The World, And Killing Us
The Kerala nurdle spill was possibly the first from a shipwreck affecting India, and brings to our doorstep a relatively unknown aspect of the global plastic pollution crisis.

Plastics are bad. We know this. They are harmful because they destroy marine life and ecosystems, and the greenhouse gases emitted in a plastic item's lifecycle contribute to global warming.
Now, the building blocks of all things plastic in our lives are tiny pellets called 'nurdles' - each no more than 5mm in diameter, or about the same size as a grain of rice. Hold one nurdle in your hand and it seems insignificant... surely something so small could hardly be dangerous.
But they are; nurdles are a worrying source of microplastic pollution.
It isn't the one nurdle that is worrying, it is the hundreds of thousands of tons of nurdles that enter the environment every year, via spills at factories they are made or at those they are melted and re-moulded to produce larger items, or, as in the case off Kerala, during transit.
What Happened In Kerala?
On May 25, 2025, a nearly 30-year-old cargo ship, the Liberia-flagged MSC Elsa, capsized and sank about 25km southwest of Kerala's Alappuzha. The ship was carrying over 600 containers.
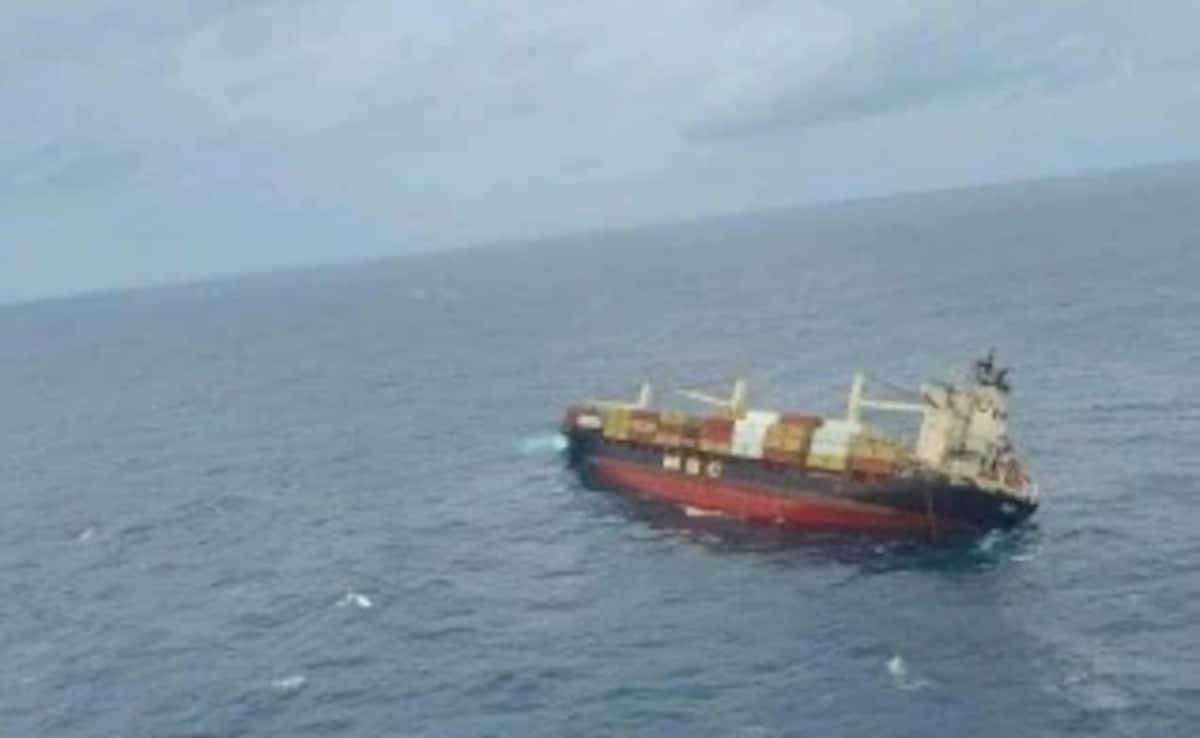

MSC Elsa, the Liberian-flagged cargo shop sinking off the Kerala coast.
The immediate worry was an oil spill that, uncontained, would have devastated the coastal ecosystem. The Coast Guard said the ship had 88.4 metric tons of diesel and 367 metric tons of furnace oil. Fortunately, 'swift action' by marine officials prevented a major spill.
Forty-eight hours later the nurdles started appearing.
Thousands, maybe tens of thousands, washed up along the coast, including near state capital Thiruvananthapuram. Many tens of thousands more probably sank or were eaten inadvertently by fish and marine organisms like turtles, and will later find their way into our bodies.
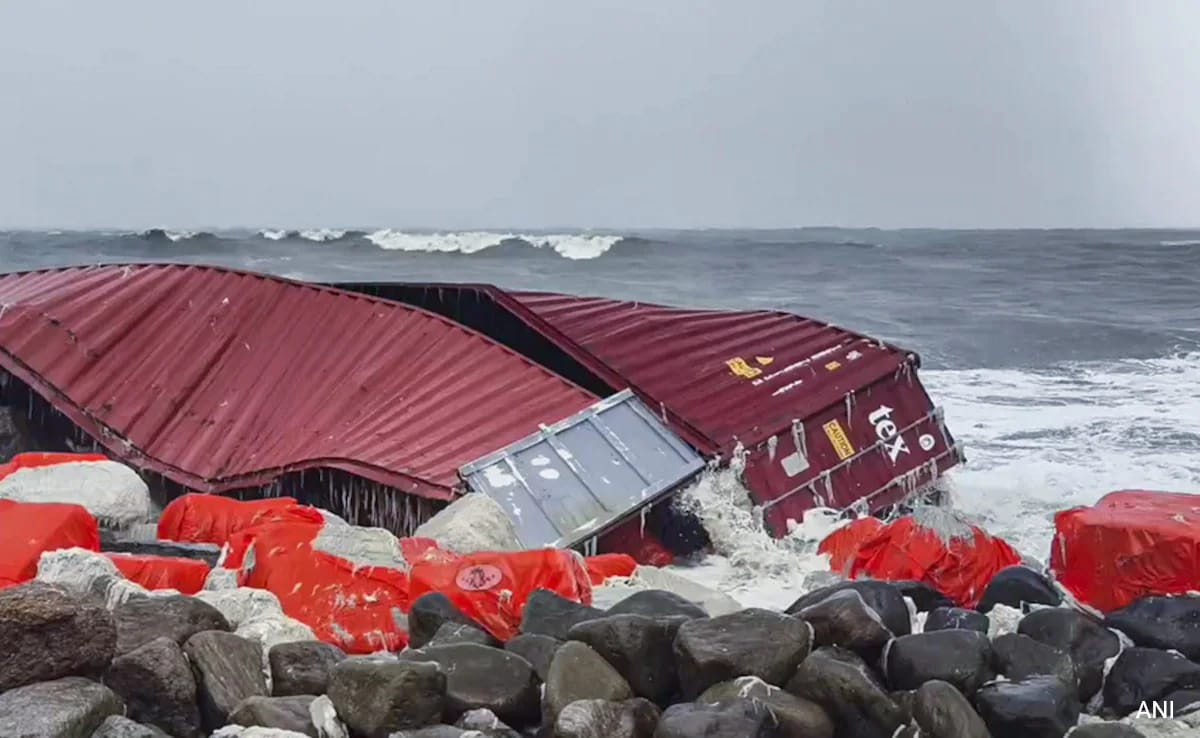

Broken cargo containers from MSC Elsa washed up along the Kerala coast
The Kerala government started a clean-up operation, with civilian volunteers, marine scientists, and local officials working together, guided by drone feeds, to identify and clear the pollution.
And fishing was stopped for 20 nautical miles, around 38km, around the shipwreck.
The size of the nurdle spill is unclear.
But the Kerala incident was possibly the first nurdle spill from a shipwreck affecting India, and brought to our doorstep a relatively unknown aspect of the global plastic pollution crisis.

Tens of thousands of nurdles have washed up on the Kerala coast.
Photo: Image posted on X by @Pugdandee
There have been 10 major spills since 2012.
The biggest was in 2021 - the X-Press Pearl, a Singapore-registered ship sank off Sri Lanka and released 1,680 tons into the Indian Ocean.
The Sri Lanka spill ravaged marine ecosystems around the island, killing fish and other sea creatures, including dolphins, and wrecking the livelihoods of coastal communities.
And then there was a spill in 2018, off South Africa. Pellets washed up on the coast of Perth in Western Australia, almost 3,000km away.
So What Is The Nurdle Crisis?
According to Fidra, a Scottish charitable organisation working on reducing plastic waste and chemical pollution, around 22.4 trillion nurdles are released into the environment every year.
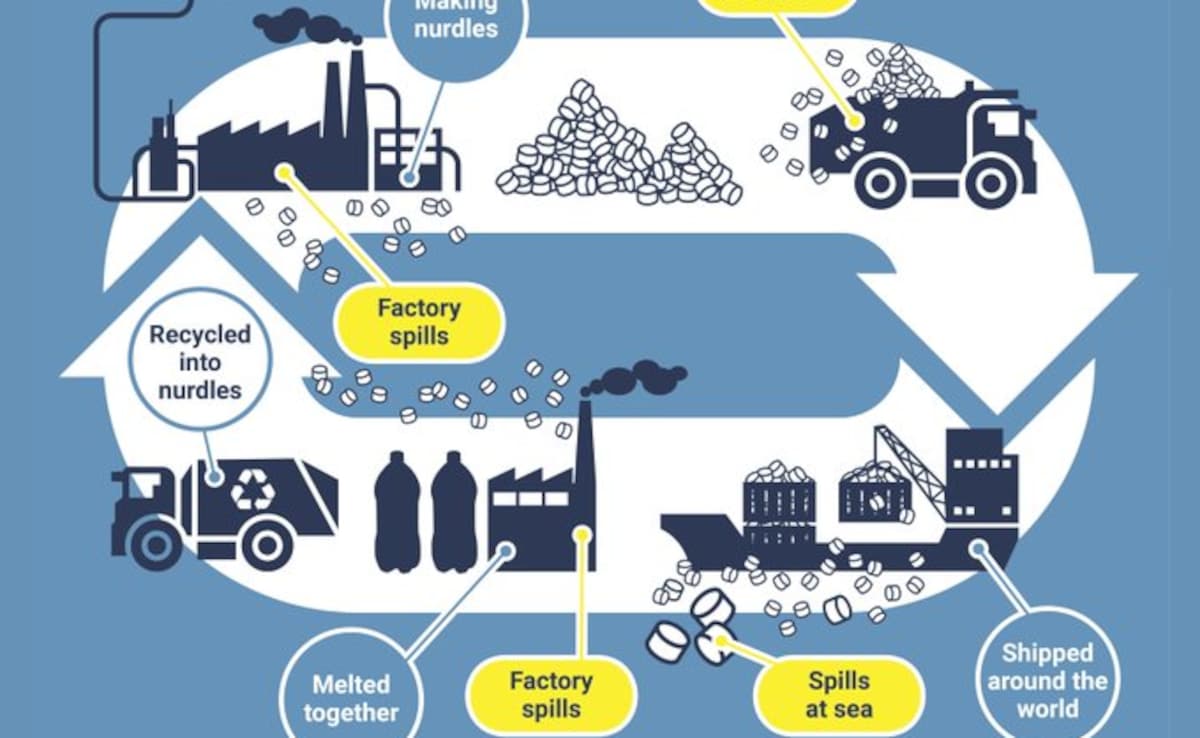
How nurdles enter the environment.
Photo Credit: Image posted on X by @greatnurdler
Nurdle spills have been reported from across the world, but there are more confirmed spills from the United States and western European nations than those in the Asia-Pacific, despite it generating an estimated 37 per cent of the world's plastic imports and 30 per cent of exports.
An assessment by Fidra indicates 41 major pellet pollution sites across the world, and cautions "this is thought to be an underestimate due to a lack of industry transparency and reporting".
Nurdle spills can have a massive impact on the health of wildlife and humans; ingested particles can cause organ damage, ulceration, and even death. In November 2024 the International Fund for Animal Welfare identified nurdles as "the most harmful pollutant".
The crisis doesn't end here. Over time nurdles break up into even smaller pieces that are then consumed by even smaller marine organisms.

How nurdles enter the food chain. Photo: nurdlehunt.org.uk
These become prey for larger creatures and the plastic you didn't eat on Monday, when you had a nice hot plate of fish fry, enters your body on Friday, because the fish you ate then is the one that ate the microorganisms that ate the smaller pieces of nurdle.
How Do We Stop This?
At the source.
Because nurdles are so tiny and there are so many of them, it is impossible/impractical to completely contain a spill, even a small one. It is far easier to go to the source - where the nurdles are made - and have each government pass and enforce laws ensuring safer production and transit protocols.
Those laws are coming, although slower than they should. Kenya, in East Africa, for example, has passed legislation against single-use plastic considered among the toughest in the world.
Chile, Canada, France, the European Union, the United Kingdom, and the United States have also passed laws restricting use of plastic and plastic items, single- or multi-use.
India has banned the production and use of single-use plastics but can, and should, do much more, starting with recognising the dangers posed by nurdles and tightening relevant rules.
NDTV is now available on WhatsApp channels. Click on the link to get all the latest updates from NDTV on your chat.

-
From Tel Aviv To Lucknow: How Space Is Uniting India And Israel
Israeli astronaut Eytan Stibbe, who flew on the Axiom 1 mission in 2022, is now extending a hand of friendship to India.
-
Opinion | IMAX-Like Churches, TikTok Gurus, Putin: Inside America's Murky 'Faith' Bazaars
Behind America's dazzling surface lies another nation - one that fasts and prays for national repentance, that warns of apocalypse, that casts out demons on TikTok and tries to raise the dead in church basements.
-
The Sinwar Plot: How Hamas Outwitted Israel, Until It Didn't
Mohammed Sinwar's death comes seven months after his brother Yahya was killed in an Israeli mission in Rafah. The Sinwar brothers' story has now ended. But central to their story is an audacious operation.
-
Opinion | Protests, Pakistan, And A Yunus-Army Showdown: Why Bangladesh Is On Edge
An embattled Gen Zaman has much to contend with, courtesy a mischievous 'Chief Advisor' who seems to be trying to ingratiate himself with multiple countries - including China - to extend his stay in office.
-
NDTV Explains: Everything About India's New 5th-Generation Stealth Fighter
India's first fifth-gen fighter will be a single-seat twin-engine jet with advanced stealth coatings and internal weapons bays like those on the US-made F-22 and F-35.
-
NDTV Ground Report: Drugs At Centre Of China's 'Three Warfares' Strategy
The Chinese fund and support Myanmar's military junta. The junta in turn hire NSCN (IM) and ZRA to fight on their behalf and provide protection to poppy fields
-
India To Dust Off 1971 War Air Base To Counter Bangladesh's China Turn
If Beijing does fund the renovation of Lalmonirhat then expect the Chinese to have military assets - fighter jets, radars, surveillance equipment, etc. - stationed there as part of the deal.
-
NDTV Explains: India vs China In Race For Arctic Oil, Gas, Shipping Routes
Unlike China, India is seen as slow-playing its Arctic card, choosing to cooperate with the Council and present itself as a 'responsible stakeholder' by engaging with all sides on key issues.
-
Opinion | No, Sirs. South Africa Is Not 'Killing' Its Whites
The "white genocide" myth serves no one. It stokes fear among white South Africans, trivialises the pain of Black South Africans, and hands a loaded weapon to racists in America and Europe.
-
News Updates
-
Featured
-
More Links
-
Follow Us On










